ID Token and Access Token: What’s the D
TABLE OF CONTENTS What Is an ID Token? What I...
Blockchain technology is rapidly changing the way people think about securing data, verifying transactions and streamlining business processes. The technology has gained widespread traction due to its ability to provide a secure and efficient platform for the storage and transfer of data. With its roots in cryptocurrency, blockchain technology is revolutionizing many industries in several ways. In this article, we will discuss the fundamentals of blockchain and its potential to change how business is done.

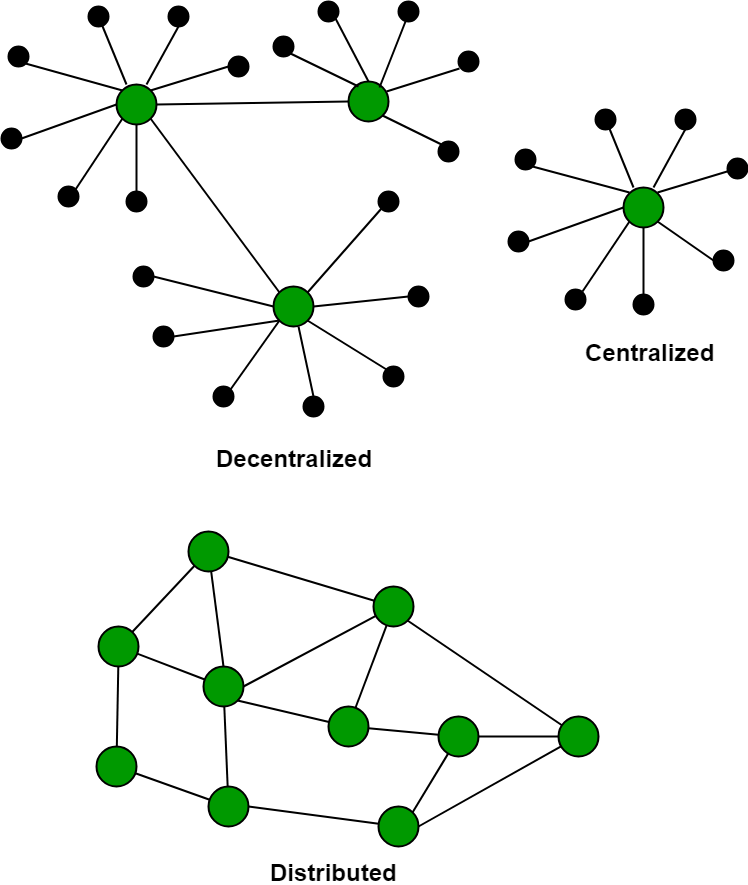
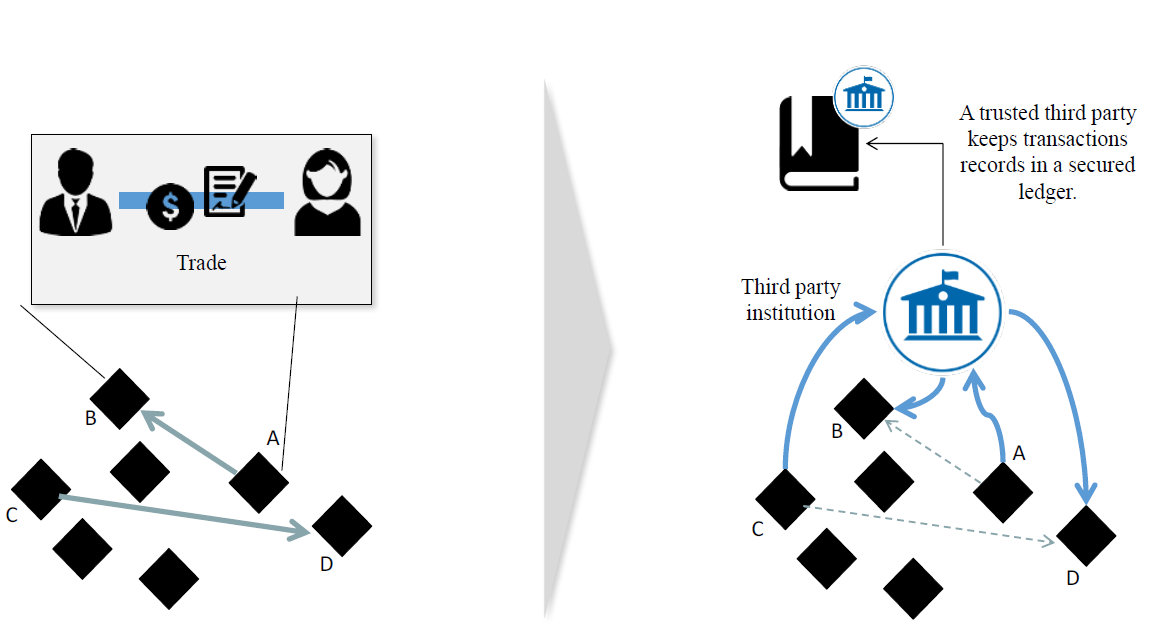
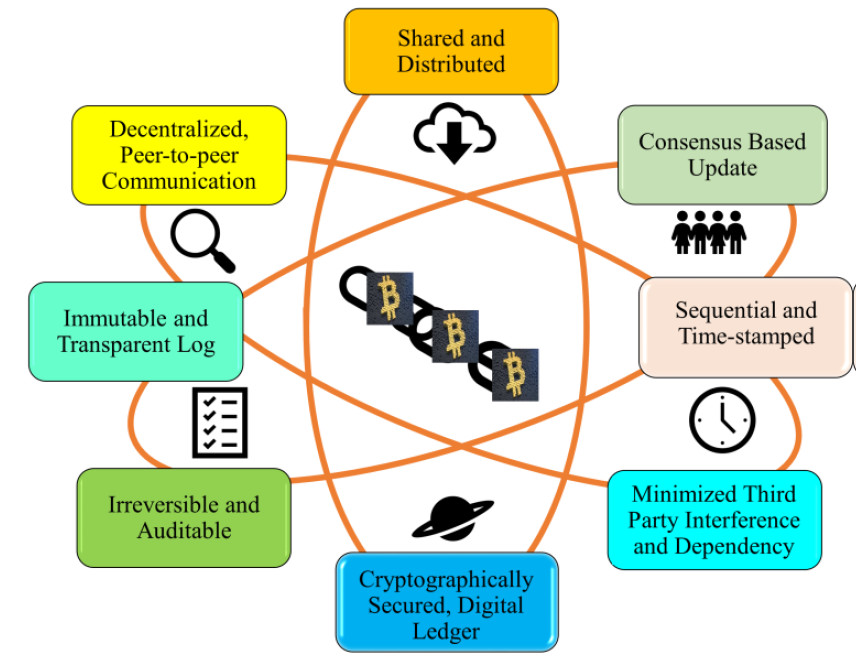
At its most basic level, blockchain is a distributed digital ledger that records transactions between two or more parties in a secure and transparent manner. Each transaction is grouped into a “block” and linked to the previous block using cryptography, making it nearly impossible to alter or tamper with the data. This means that all participants can view and confirm the accuracy of the chain of data at any time.
The underlying principle behind blockchain is decentralization, which means that there is no central authority controlling or verifying transactions. Instead, the system relies on a consensus protocol where all participants agree to an agreed-upon set of rules, known as consensus algorithms, in order to validate each transaction. This system allows for more trust between parties compared to traditional financial networks, where one party verifies the accuracy of transactions.
One of the key benefits of blockchain technology is enhanced security. By storing information in blocks, it becomes virtually impossible for hackers to access data without permission from each participant in the network. Furthermore, each block contains a unique cryptographic signature, which makes it impossible for malicious actors to forge documents or alter existing ones without being detected.
In addition, blockchain technology helps improve efficiency by drastically reducing wait times for transactions to be validated and completed. The technology enables faster and more secure payments which in turn reduces costs associated with transaction processing fees.
Blockchain is also well suited for implementing smart contracts between two or more parties. A smart contract is simply a computer protocol that enforces the performance of an agreement automatically. This means that when certain conditions are met, an automated response is triggered in order to execute the terms of the agreement. This process eliminates the need for third-party intermediaries such as banks or other financial institutions to verify transactions and can significantly reduce costs associated with traditional contracts.
The use of blockchain technology is not limited to the financial industry; it has potential applications across a wide range of industries including healthcare, agriculture, supply chain management, energy trading and governance models. With its revolutionary potential to transform how businesses operate, there are huge opportunities for companies to create new products and services that leverage this technology.
It remains to be seen how far reaching the implications of blockchain technology will be for businesses in the future. However, one thing is certain: blockchain has laid the foundation for a new era of decentralized data infrastructure that promises greater transparency, trust and efficiency.
Blockchain technology is a revolutionary technology that has been gaining traction in the industry and is revolutionizing many aspects of our lives. Blockchain is a distributed and decentralized digital ledger, that records transactions in a secure and chronological manner across multiple computers and provides a platform for various applications such as cryptocurrencies, smart contracts, digital identity, and much more.
II. Overview
Blockchain technology has a wide range of potential applications. At its core, a blockchain is a decentralized and distributed digital ledger, with entries stored in cryptographically secured blocks. Each block contains the digital records of transactions that have taken place, with the most recent transaction appearing at the top. This allows for faster and more transparent verification of transactions as there is no need for any third-party verification. In addition to this, blockchain technology also offers other benefits such as improved security through the use of cryptography and decentralization which makes tampering with the system difficult.
III. Advantages
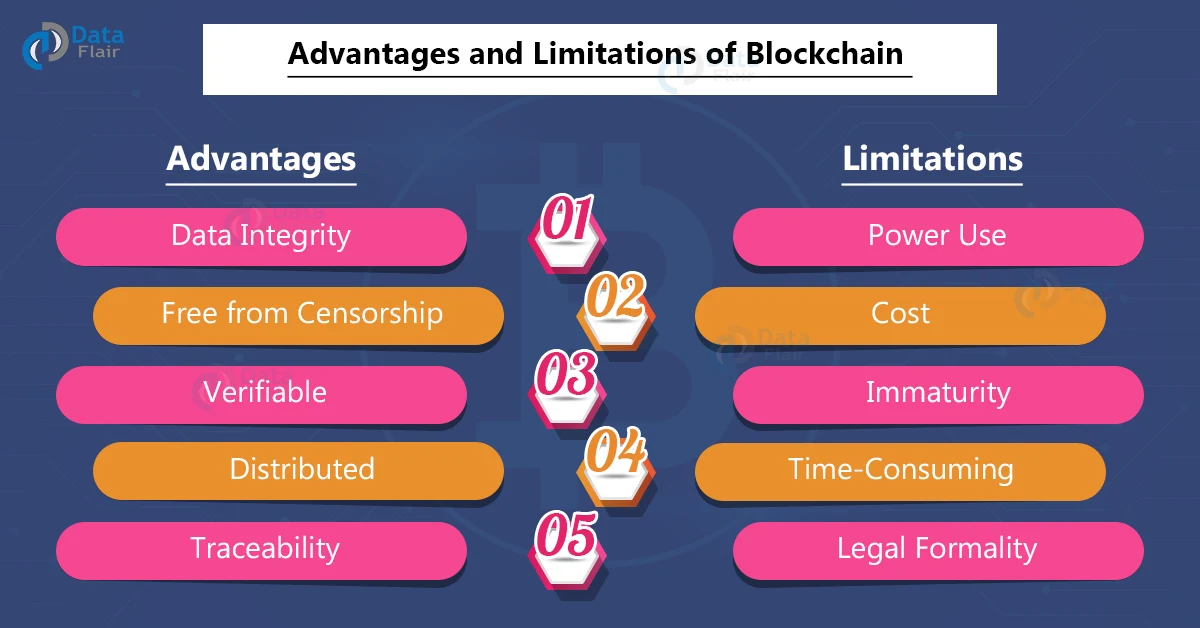
The advantages of blockchain technology are numerous. It offers an immutable public ledger, which allows for transparent tracking of all transactions taking place on the blockchain. Additionally, blockchain technology provides increased security through enhanced cryptography and decentralization. Furthermore, since it is open source, it allows for cost savings by eliminating middlemen and reducing transaction fees. Finally, its distributed nature makes it resilient to outages, ensuring continuous operation even in case of system failure.
IV. Disadvantages
Despite the numerous advantages that blockchain offers, there are also some drawbacks to consider. For instance, blockchain technology can be slow and resource-intensive due to its distributed nature. This can lead to scalability issues, making it difficult to handle high volumes of transactions. Additionally, the implementation of blockchain technology can be costly and require specialized workforce. Finally, due to its volatility, there is always the potential for cryptocurrency coins to lose value quickly.
V. Conclusion
In conclusion, blockchain technology offers many potential applications in the financial services industry. Its secure and transparent nature makes it ideal for a variety of applications such as cryptocurrency trading and smart contracts. Although there are some drawbacks associated with it, its widespread adoption suggests that these issues can be addressed with further development. As the technology continues to evolve, we are likely to see its usage expand even further in the near future.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/cryptocurrency.asp-final-11275c98371247efad3e5179ae6e7d7e.jpg-75078b39349443e7bb412213be0c6dc3.jpg)
Blockchain is a revolutionary technology that is revolutionizing the way information is stored, managed and transacted. It is a distributed public ledger or database that stores data in a network of computers, rather than in a single location. The data stored in the blockchain is immutable and tamper-proof, making it virtually impossible to alter without the consent of all participants in the blockchain.
Blockchain technology offers unparalleled security, transparency and immutability, which is why it is being adopted by so many organizations. This distributed ledger can record all kinds of transactions with accuracy and complete traceability. It also provides an effective platform for designing, building and deploying applications that are reliable, decentralized and secure.
At its most basic, blockchain is a chain of digital blocks that store information about transactions or data sets. The blocks are linked together using cryptography, making the chain of blocks secure and tamper-proof. Each block contains data about the previous block and a timestamp, making it impossible to go back and alter previous records. Additionally, since the data is stored on multiple computers in a distributed manner, it increases the security of the data.
In conclusion, blockchain is a revolutionary technology that has the potential to revolutionize many industries. With its features of transparency, security, and immutability, blockchain offers numerous advantages over traditional methods of data storage and management. As more organizations begin to adopt this technology, we can expect to see wide-scale changes in how data is managed in the future.
Blockchain technology is a revolutionary breakthrough in data storage, accounting, and transaction processing. It is a distributed ledger that can track digital assets and record network transactions, enabling a distributed network of computers to keep a secure, transparent record of all digital transactions. Blockchain is being heralded as the future of commerce and financial services, as it can dispense with physical paperwork, reduce fraud and corruption, and increase the speed of payments.
At its core, blockchain is a growing list of records, called blocks, that are connected using cryptography. Each block contains a cryptographic hash of the previous block, a timestamp, and transaction data. By design, it is resistant to data modification and secure from tampering or hacking. Hence, it provides an ideal platform to store and manage sensitive information with maximum security.
The distributed nature of blockchain also makes it suitable for multiple parties to carry out transactions without relying on a centralized intermediary, like a bank or government agency. This offers several benefits such as larger data availability, faster transactions, improved traceability, and enhanced transparency.
For businesses, the advantages of blockchain include cost reduction, improved scalability and efficiency, increased trust between parties, and enhanced accountability. For example, real estate property ownership transfers can be securely tracked via blockchain to record title registration and any changes in ownership. In financial services, blockchain can be used to increase speed and accuracy of payments while reducing transaction fees significantly.
The possibilities of blockchain don’t just end here—it has been explored in various industries such as healthcare, government services and supply chain management. And with every passing day, new applications are being explored for its potential use.
It is no doubt that blockchain is set to revolutionize the way businesses operate in the future and change the way we interact with each other through digital asset transfers and smart contracts. The technology has the potential to secure data from hackers and reduce the risk of cyber attacks while minimizing the costs associated with fraud prevention processes. With such great potentials ahead and ongoing developments in this technology, it’s safe to say that blockchain will continue to shape our future world!
As one of the most innovative technologies of our time, Blockchain has garnered much attention due to its wide range of potential benefits. The technology is gaining ground with more and more companies adopting it in their operations and processes. This is all thanks to the numerous advantages that Blockchain provides for businesses and users alike.
From financial transactions to identity protection, Blockchain offers a selection of advantages that can benefit any business. Here are some of the main benefits of incorporating Blockchain into a business.
Secure Transactions: One of the primary advantages of using Blockchain is the security it offers for transactional processes. By using peer-to-peer networks to create and store records, these records cannot be manipulated or changed without the consent of all parties involved. This makes it ideal for businesses that carry out digital payments as well as other sensitive data transfers.
Cost-Effective Solutions: Another major benefit of leveraging Blockchain in a business is its cost-effectiveness. With its encrypted system, businesses can avoid incurring additional costs associated with third party intermediaries such as banks, payment processors and settlement services. This not only makes the process easier and more efficient, but it also helps keep costs down.
Enhanced Data Security: The decentralized nature of Blockchain also ensures enhanced data security. With its system of ledgers and consensus protocols, businesses can achieve a degree of transparency that would otherwise not be possible with traditional systems. This is because the data stored on the blockchain is distributed across many computers, making it nearly impossible to hack into or modify without all parties agreeing on the changes made.
Improved Efficiency: The use of Blockchain in businesses also promotes efficiency. As Blockchain eliminates the need to use manual processes for verifying and validating transactions, businesses are able to speed up their operations and streamline their processes. This improved efficiency enables them to better serve their customers and achieve better results overall.
With so many benefits, there is no doubt that Blockchains will continue to grow in popularity and usefulness among businesses. From enhancing data security to providing greater cost savings, Blockchain offers a host of advantages that cannot be achieved by traditional methods. As such, it is essential for businesses to explore the potential of this innovative technology in order to reap its full benefits.

Blockchain technology is quickly becoming one of the most widely used tools for secure data transactions and storage. As more organizations and individuals embrace blockchain, security has become an increasingly important factor for many users. Increased security for blockchain is essential in order to ensure that the data and transactions are safe from tampering, theft, or other malicious activities.
The primary benefit of blockchain is its ability to provide secure, immutable, and transparent transactions. By using a decentralized network of computers, it is nearly impossible for any one individual or group to access or modify the data stored on the blockchain. In addition, the use of cryptographic algorithms provides a high level of security by ensuring only authorized users can access the data.
To further improve security, blockchain users can utilize multiple layers of encryption to protect the data stored on their distributed ledger. This includes encrypting data when it is stored in the blockchain as well as when it is transmitted between nodes. Additionally, certain consensus mechanisms can be used to verify transactions are occurring correctly and without tampering. For example, proof-of-work and proof-of-stake are common consensus mechanisms that can be used to validate transactions before they are recorded on the blockchain.
In addition to improved encryption and consensus mechanisms, increased security for blockchain also involves better authentication practices. This includes using strong passwords as well as two-factor authentication (2FA) to add an extra layer of security in verifying users’ identities before they can access or modify the data stored in the blockchain. Additionally, organizations should consider implementing identity management systems to ensure only authorized individuals have access to sensitive data or transaction histories.
Finally, blockchain organizations must ensure their networks are configured properly and kept up-to-date with the latest security measures. This includes regularly patching any known vulnerabilities, using secure hosting services when available, and implementing a comprehensive system of auditing and monitoring to detect any suspicious activity.
Overall, increased security for blockchain is essential in order to ensure organizations and users can securely store and transact data without fear of tampering or theft. By utilizing multiple layers of encryption, consensus mechanisms, identity management systems, and secure hosting services, organizations can ensure their data is kept safe and secure on the blockchain network.

The development and implementation of blockchain technology has revolutionized the financial and digital industries, offering businesses a secure, decentralized way to store and transfer data, as well as increase efficiency. But while blockchain technology continues to improve with each iteration, blockchain developers are now working on ways to further increase the efficiency of their distributed ledger. Here’s an overview of how improved efficiency is being attained with blockchain:
1. Optimizing Consensus Algorithms
The consensus algorithm is one of the most important aspects of any blockchain platform, as it is what allows multiple computers on the network to arrive at a consensus when verifying data. In its current form, the traditional consensus algorithms employed by most blockchains can be slow and inefficient. To address this issue, developers are turning to improved consensus algorithms like proof-of-stake and delegated proof-of-stake. These algorithms allow transactions to be verified faster and more securely than traditional consensus algorithms, making them ideal for applications that require high levels of speed and security.
2. Increasing Throughput Capacity
Throughput capacity is another key component of blockchain technology, as it determines how quickly a given blockchain can process transactions. While many blockchains already have impressive throughput capacity, developers are always looking for ways to make the process even faster. Some methods for increasing throughput include increasing block size and utilizing different forms of sharding and parallelization techniques. With improved throughput, businesses are able to reduce transaction costs and drastically reduce the amount of time it takes to transfer data.
3. Utilizing Sidechains
Another way blockchain developers are working to increase efficiency is by utilizing sidechains in certain applications. Sidechains are separate blockchains that are connected to the main blockchain platform, allowing developers to move certain types of data or transactions off the main Ethereum network and onto a dedicated sidechain platform. By utilizing sidechains, developers can save resources on the main chain while still ensuring that data is stored securely and is fully decentralized.
While blockchain technology is already incredibly efficient, developers are constantly working to make it even better. By optimizing consensus algorithms, increasing throughput capacity, and utilizing sidechains, they are able to create a blockchain network that can scale quickly and handle a large volume of transactions without sacrificing speed or security. As these improvements continue to be implemented, businesses will be able to further utilize the power of blockchain technology in a wide range of applications.
In today’s digital world, blockchain technology is becoming increasingly popular. It is becoming more and more commonplace in businesses and the public sector, as it offers a secure and efficient method for tracking transactions and storing data. However, the costs associated with running a blockchain network can be a barrier to entry for many businesses. Fortunately, there are various ways to reduce costs for blockchain networks, allowing companies to take advantage of the benefits of this technology without breaking the bank.
The first way to reduce costs for blockchain networks is to look at the various private blockchains currently available. In contrast to public networks, these private networks are managed by a single organization and are not accessible to the public. As such, they require much less computing power and energy to operate, making them significantly cheaper than public networks. Additionally, they can be tailored to meet the specific needs of the organization.
Another way to reduce costs is by using alternative consensus mechanisms. While most blockchains use proof-of-work (POW) consensus mechanisms, there are other alternatives out there that may be cheaper. For instance, proof-of-stake (POS) is an alternative that uses fewer resources and is faster than POW. Additionally, there are several new consensus protocols being developed which are specifically designed to increase efficiency and reduce costs.
Additionally, businesses can save money on storage costs by using distributed file storage systems. These systems allow users to store data on multiple computers rather than one, which reduces the cost associated with maintaining a large server or cloud system. Additionally, these systems generally offer greater security than traditional storage methods.
Finally, businesses can save money by taking advantage of the various blockchain tools available. There are now a variety of software tools which allow businesses to easily develop and manage their own blockchain applications. These tools often have built-in features to reduce costs, such as automation and cost optimization algorithms.
In conclusion, there are various ways for businesses to reduce their costs associated with running a blockchain network. By exploring the various private blockchains available, as well as alternative consensus mechanisms, distributed file storage systems, and blockchain development tools, businesses can take advantage of the benefits of this technology without having to invest in expensive infrastructure projects.
Blockchain technology is one of the most revolutionary technologies to emerge in recent years. It is a decentralized, distributed digital ledger that records transactions and assets across a peer-to-peer network. Blockchain technology has the potential to transform many industries, from finance to healthcare and more.
There are several types of blockchain available for use, each with unique characteristics and features to meet the needs of different industries. Below, we’ll explore the different types of blockchain solutions and how they work.
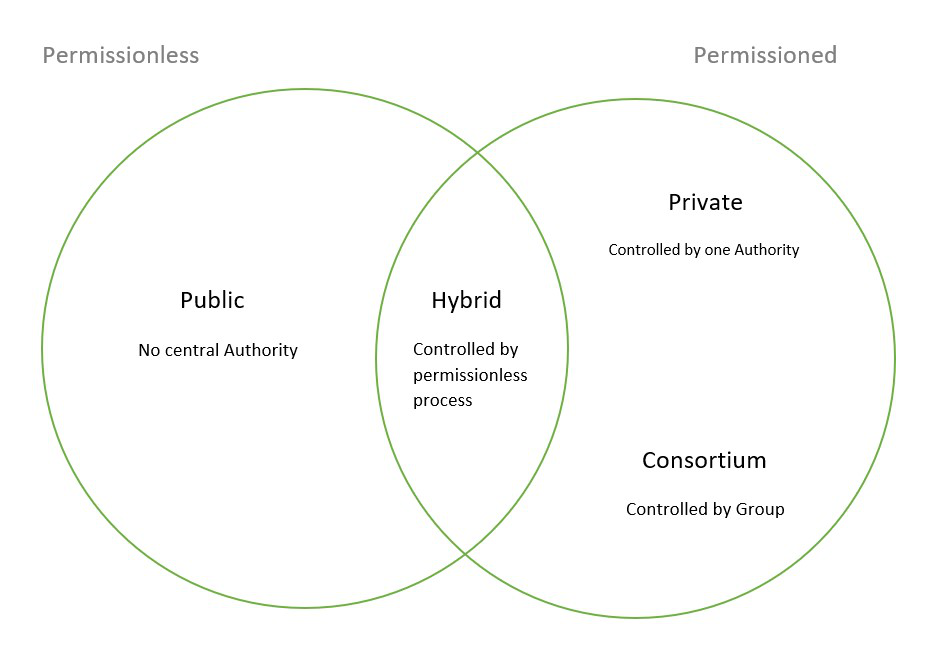
Public Blockchains:
Public blockchains, such as Bitcoin and Ethereum, are open-source and permissionless. This means anyone can join, view and validate the ledger. These solutions are highly secure and offer a high level of transparency.
Private Blockchains:
Private blockchains are permissioned solutions, meaning only invited users can access the platform and no one else can view or tamper with the data in any way. These solutions are useful for businesses that need to keep track of confidential data but still have the benefits of blockchain technology.
Federated or Consortium Blockchains:
Federated or consortium blockchains are another type of permissioned blockchain. These solutions require agreement between several parties to authenticate transactions. They are useful for industries that require multiple points of verification, such as banking or healthcare.
Hybrid Blockchains:
Hybrid blockchains combine the features of public and private blockchains. They allow for restricted access, meaning only certain entities can view their data. At the same time, they also provide transparency, allowing users to view the data on the ledger if they are authorized.
Sidechain Blockchains:
Sidechain blockchains are secondary blockchains that run alongside a primary blockchain. They are used to improve scalability and reduce transaction costs by taking certain tasks off of the mainchain.
Programmable Blockchains:
Programmable blockchains are blockchains that allow users to write their own smart contracts and execute them on the blockchain. They are becoming increasingly popular as developers look for ways to create decentralized applications (DApps).
With all these different types of blockchain available, it’s important to understand their differences and pick the right one for your business needs. Depending on your industry and goals, you may find that one type of blockchain is more suitable than another. In any case, it’s important to do your research before investing in any blockchain solution so that you make sure you’re making the right decision for your business.

Public Blockchain is one of the most popular forms of blockchain technology. It is a type of blockchain that is open to the public, where anyone can view transactions that have taken place on the network. A public blockchain is a distributed ledger technology (DLT) that enables users to anonymously and securely share and store information without the need for a central authority.
The purpose of a public blockchain is to be completely open and transparent, allowing anyone to join and view the blockchain data. This means anyone can view and see for themselves what is happening on the network, providing transparency which is invaluable in an increasingly digital world. This also means anyone can participate in transactions that take place on the network, allowing for more widespread adoption and use of the technology.
Public blockchains are becoming increasingly popular due to their ability to provide greater decentralization than their private counterparts. Decentralization is crucial for a secure network since the data is not held in one place, making it much more difficult to manipulate or tamper with.
Additionally, public blockchains are attractive to businesses due to their lower transaction costs and faster transaction speeds. This makes them much more cost-effective than private blockchains, which often require fees for each transaction. Furthermore, public blockchains can be used to facilitate smart contracts without requiring a third-party intermediary, allowing for increased efficiency and security in transactions.
Overall, public blockchains are becoming increasingly popular as more people become aware of their benefits. They provide a secure, decentralized platform which allows anyone to participate in transactions while providing greater transparency and trust. Additionally, they offer lower transaction costs and faster transaction speeds, making them much more cost-effective than private blockchains. As such, public blockchains are set to become even more widely adopted in the future as businesses continue to explore their potential applications.

Private Blockchain is an emerging form of digital ledger technology known as blockchain. It is a type of database system that allows the same data to be stored across multiple nodes or parties, while ensuring the highest level of security and privacy. Unlike public blockchains which are open to anyone, private blockchains offer an exclusive platform to organizations or specific groups of users.
The advantage of a private blockchain over a public blockchain is that it offers more control over the management of data. This makes it an ideal solution for enterprise solutions where data privacy is essential. Private blockchains are often referred to as ‘permissioned’. This means that in order to access the ledger, an invitation or permission must be obtained from the owners of the ledger.
Private blockchains offer numerous benefits such as enhanced control, privacy and scalability. These properties make it an efficient way to manage large databases that involve exchange of confidential information. It also provides users with a faster transaction rate compared to public blockchains. Additionally, private blockchains have an improved consensus algorithm, which makes them more secure than public blockchains.
Furthermore, private blockchains have the potential to reduce costs. They can help organizations automate their business processes and improve efficiency by reducing manual intervention and paperwork. By eliminating the need for third-party vendors, these systems can significantly reduce transaction costs and result in cost savings.
However, there are some drawbacks to private blockchains. Private blockchains are limited in terms of scalability since they are only accessible by a select group of participants. In addition, they lack the same level of decentralization and transparency seen in public blockchains since they are operated and maintained by a single entity.
Overall, private blockchains can be a great option for organizations looking to securely store confidential data or automate their business processes. With its enhanced security, privacy and scalability features, it can help organizations achieve efficiency gains in the long run.

A consortium blockchain, also known as a federated blockchain, is an alternative approach to distributed ledger technology designed to be more secure and efficient than other types of blockchain networks. This type of blockchain combines private and public characteristics and allows only pre-approved participants to access the ledger and validate transactions.
Consortium blockchains are ideal for networks in which a group of entities needs to collaborate while still maintaining autonomy and control over the network data. This structure requires the consensus of multiple parties and can be used for supply chain management, financial services, healthcare, energy, and more.
Unlike public blockchain networks, consortium blockchains are private networks run by a central authority. This authority has the power to control membership and decide which entities are authorized to transact on the network. The number of participants generally ranges between two and 20, so these blockchains offer more control than permissionless public networks.
Consortium blockchains offer various benefits over public networks. One key advantage is the improved speed and efficiency of transaction validation. In a consortium network, the pre-defined nodes must come to agreement before any transaction can be validated, resulting in quicker confirmation times than in a public network. The consensus process also results in more secure transactions because it requires multiple parties to agree before any changes can be made to the ledger.
In addition, consortium blockchains offer greater scalability. When compared to public networks, consortium blockchains can support more transactions per second due to their smaller size and fewer participants. This makes them well-suited for high volume applications such as finance and healthcare.
However, there are also drawbacks associated with consortium blockchains. For instance, they lack the decentralization of public blockchains, making them vulnerable to malicious actors who manage the network or its participants. In addition, since only certain parties can access the blockchain, it can be difficult for new entities to join the network.
Overall, consortium blockchains offer a variety of advantages and disadvantages that must be weighed when deciding whether or not this type of network is suitable for a given application. For companies looking to securely transact with limited partners, this type of distributed ledger technology offers a great solution.

Blockchain is a revolutionary technology that has the potential to revolutionize our lives. It has already impacted several industries, including finance and healthcare, and shows great promise for further use in the future. While many people don’t understand the full scope of what blockchain entails, understanding its various components can help us gain a better understanding of the technology.
In this article, we’ll take a look at the main components of blockchain and how they come together to form a secure and reliable network.
A blockchain is composed of two main components: nodes and blocks. Nodes are computers or devices connected to the network that store, validate, and propagate new data to other nodes. Blocks are groups of data stored on the nodes which contain information such as transaction records or smart contracts. Each block contains a cryptographic hash of the previous block, allowing a chain of blocks to be created and linked together. This makes it almost impossible to change data stored in a particular block without changing all the blocks after it.
The consensus mechanism is another key component of blockchain technology and is an essential part of any blockchain project. It is the process used by nodes to agree on the veracity of data stored on the network. Different consensus models exist, with some of the most popular being proof-of-work (PoW), proof-of-stake (PoS), and delegated proof-of-stake (dPoS).
Privacy is also an important element of blockchain technology, both for individual users and for businesses alike. The use of public-key cryptography allows users to securely store sensitive data on the blockchain while remaining anonymous. Additionally, privacy protocols such as ring signatures and zero-knowledge proofs can be used to ensure transaction privacy while still allowing transactions to be recorded on the ledger.
Finally, smart contracts are a powerful tool enabled by blockchain technology which allow users to create executable programs that run automatically when preset conditions are met. Smart contracts allow users to automate various processes such as payments or asset transfers, providing an additional layer of security and trust.
In summary, understanding the components of blockchain technology can provide us with a better understanding of the power of this revolutionary technology and all that it can offer. The combination of nodes, blocks, consensus mechanisms, privacy protocols, and smart contracts allows us to build secure and reliable networks which have far-reaching implications for our society.

Nodes are an integral component of blockchain technology, serving as the backbone for this revolutionary new way to store and transfer data. A node is a computer that is connected to the blockchain network and helps to maintain the network’s shared ledger. Nodes broadcast, validate and propagate transactions across the network. In essence, nodes are responsible for keeping the blockchain functioning and secure.
There are two types of nodes in a blockchain network: full nodes and lightweight nodes. Full nodes are computers that hold a complete copy of the blockchain ledger, whereas lightweight nodes are much smaller in size and only store portions of the ledger. Both types of nodes can be used to verify transactions, so they all play a vital role in ensuring the accuracy and security of the blockchain.
The role of node owners is to provide their computing power to validate transactions and ensure that all participants in the network have a consistent view of the blockchain data. This is known as consensus and is an essential part of blockchain technology. Node owners are incentivized with rewards such as cryptocurrency or tokens when they contribute their computing power to the network.
In summary, nodes are critical components of any blockchain network and they provide the necessary infrastructure to ensure its smooth operation. Node operators earn rewards for helping to maintain the security and accuracy of the blockchain by verifying transactions, thus making it an attractive proposition for tech-savvy individuals. As blockchain technology continues to grow, more individuals will join the network as nodes so that the network remains secure and reliable.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/TermDefinitions_Proof_Of_Stake_V2-4f2bd59e89e040ed9a1942761536ad45.jpg)
Blockchain is a form of distributed ledger technology (DLT) that is slowly revolutionizing the way transactions are executed. The technology is best known for its role in the fintech sector. It is a decentralized, digital platform that securely records and stores all kinds of transactions, including financial transactions.
Blocks are the most essential components of blockchain networks. Blocks are digital records of the transactions that take place on the network. Every new transaction is added to the blockchain as a new block. Each block contains a hash, or cryptographic signature, that identifies it and links it with other blocks. This cryptographic link ensures that no one can modify or delete blocks from the chain. In addition, each new block includes a timestamp that indicates when it was added to the chain.
The blockchain is secure by design because it utilizes a distributed network where information is stored in multiple places at once. This decentralization allows for a consensus mechanism to ensure the integrity of the data. Each node in the network must approve the transaction before it is added to the blockchain. This process adds an extra layer of security and helps to prevent fraud.
Blocks are also immutable, meaning they cannot be changed once they are added to the blockchain. This immutability makes it virtually impossible for anyone to tamper with the data stored within a block. Additionally, blocks contain a public ledger that anyone can view, ensuring transparency and accountability in all transactions carried out on the network.
Blockchain technology has many potential applications beyond just cryptocurrency transactions. It can be used for various industries such as healthcare records, identity verification, and digital payments. With its numerous benefits, blockchain technology will continue to expand and change how businesses operate and transact in the near future.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/cryptocurrency.asp-final-11275c98371247efad3e5179ae6e7d7e.jpg-75078b39349443e7bb412213be0c6dc3.jpg)
Cryptography is a key component of blockchain technology. It is a toolbox of mathematical algorithms that can be used to protect data and digital assets. Cryptography enables secure communications, proof of ownership, and secure storage of data on the blockchain.
Cryptography is a process of converting plain text into meaningful symbols which can only be interpreted by an intended recipient- thus ensuring data security. It works by using two mathematical algorithms: encryption and decryption. Encryption transforms plain text into meaningless symbols using a “key” that only the intended recipient has access to, while decryption uses the same key to transform the symbols back into plain text.
Cryptography is used for several reasons within blockchain technology. Firstly, it allows for secure communication between nodes in a distributed network such as the blockchain. Messages are encrypted before being sent on the blockchain and can only be decrypted after being received. This ensures that malicious actors cannot intercept or alter data in transit. Secondly, it allows users to prove they possess a digital asset. Cryptographic signatures allow users to verify their identity and prove that they own the asset they are sending.
Finally, cryptography is used to secure data stored on the blockchain. Encrypted data is stored on each node and only those with a valid “key” can view and modify it. This prevents unauthorized access and manipulation of stored data on the blockchain.
Cryptography is an essential tool in guaranteeing security on the blockchain. Without this toolbox of algorithms, the decentralized nature of blockchain networks would not exist. As such, it serves as an integral part of the integrity and security of any blockchain-based application or system.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/smart-contracts_final-0ccc5e1e4b0d4a7a95d041da2ff582e1.png)
Smart contracts are rapidly gaining a foothold in the blockchain world. The technology has made it possible to securely and efficiently store and exchange data across multiple parties. Smart contracts are computer protocols that securely facilitate, verify, or enforce the negotiation or performance of a contract.
At the most basic level, a smart contract works by inputting parameters, such as two or more contractual parties, into a computer program. When the parties enter their information into the program, the protocol will evaluate the parameters and, if they match the criteria, execute the transaction that has been programmed into the contract. This process is known as self-executing, meaning that the contract is automatically triggered when certain conditions are met.
Smart contracts can be used in a variety of different situations, including financial transactions, voting, music streaming and intellectual property rights management. For example, a smart contract could be used for a real estate transaction. In this instance, both parties would enter their information as parameters and then perform an escrow transaction where payment is released when all conditions have been met. This ensures that both parties comply with the terms of the contract and eliminates the need for third-party involvement.
The benefits of smart contracts are substantial. By eliminating third-party intermediaries from the equation, not only does it reduce overhead costs but it also makes the entire process faster and more efficient. It is also secure since it is decentralized and immutable – meaning that once a transaction is recorded on the blockchain, it cannot be undone. Additionally, smart contracts require less paperwork, making them more cost effective.
Overall, smart contracts offer an innovative way to streamline existing processes and create new ones. By providing greater security, transparency and automation within existing systems, they can help increase efficiency while reducing costs. As more businesses embrace blockchain and digital ledger technology, there’s no doubt that smart contracts will become even more common.

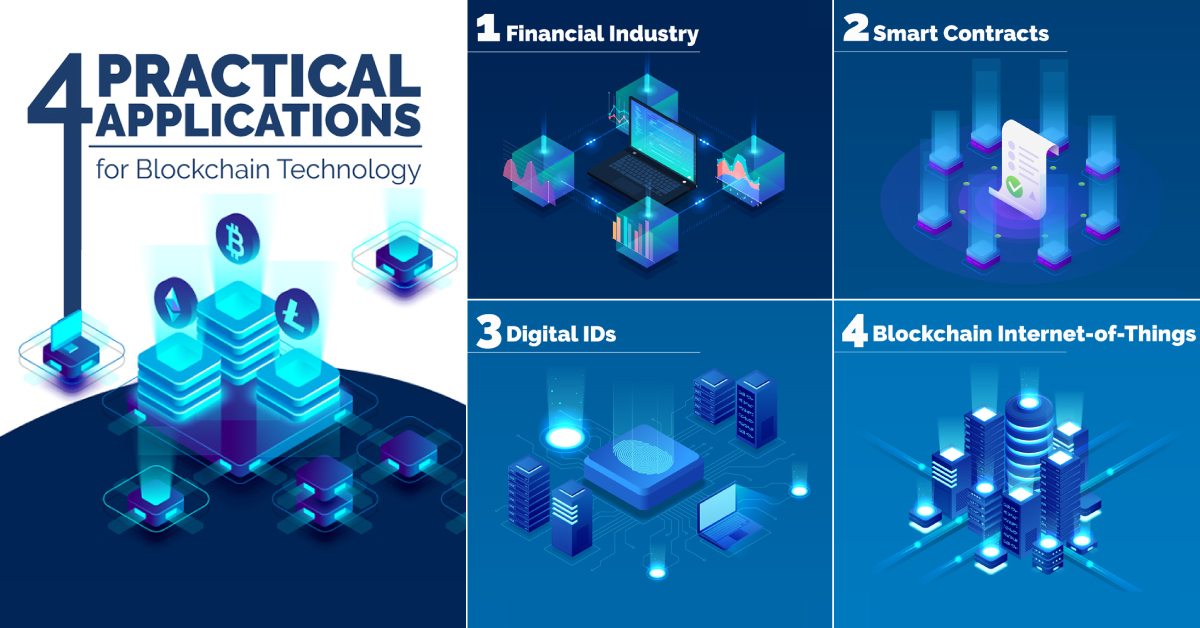
Blockchain technology has revolutionized the way transactions and other tasks are performed in the digital world. Blockchain is a distributed ledger technology that allows secure and transparent transfer of digital assets. It is a revolutionary technology with a range of potential applications which can have a profound impact on various areas. Here, we discuss some of the potential applications of blockchain technology.
1. Banking and Financial Services: Blockchain technology has potential applications in the banking and financial services sector. Banks are using this technology for their internal processes such as recording of secure payments, reducing frauds, and so on. Moreover, blockchain can also be used for international remittance and foreign exchange services, digital identity management, compliance management, and others.
2. Supply Chain Management: Blockchain can provide an immutable record of transactions that occur within the supply chain. This helps in better traceability of goods from procuring raw materials to its end use. This ensures that all the parties involved are aware of the entire process, which increases transparency and enhances trust within the system.
3. Healthcare: Healthcare systems can benefit significantly with blockchain technology. It can help to securely store patient records and medical records of patients, allowing authorized personnel to access them easily. Furthermore, it can also help to track the flow of medical supplies across different locations and ensure quality control of medical products.
4. Government: Governments can use blockchain technology to store information pertaining to citizens such as personal data, taxation details, etc., in a secure manner. Moreover, it can also come handy in voting systems as votes can be collected and stored in a distributed ledger in real time.
5. Cyber Security: Blockchain can be used to create secure networks where only authenticated users are allowed to access the network and resources contained therein. This will help combat cyber attacks such as hacking, phishing, malware, ransomware, etc., by providing an extra layer of security to the system.
In conclusion, blockchain technology has countless applications and its potential is far from being explored completely. From banking to healthcare, government to cyber security, it has a wide range of applications which will continue to expand as the technology matures over time.

Financial services are the services that are provided to individuals, businesses and governments to manage their financial needs. With the emergence of blockchain technology, digital financial services have become a part of everyday life. Blockchain-based financial services are digital and secure platforms that enable users to securely trade cryptocurrencies, store digital currencies and transact with digital assets.
Blockchain-based financial services have gained rapid traction in recent years. As more people move towards digital payments, blockchain technology is becoming an important financial service provider for users. This is because it offers users a high level of security and transparency. By removing unnecessary steps from transactions, blockchain technology ensures fast and secure transactions with minimal risk. In addition, blockchain eliminates the need for third-party intermediaries, allowing users to make direct payments to each other.
There are a number of different types of financial services available through blockchain technology. These include cryptocurrency exchanges, peer-to-peer transactions, funds transfers, payment processors and smart contracts. Cryptocurrency exchanges are platforms that allow users to exchange one cryptocurrency for another. Peer-to-peer transactions are transactions that take place directly between two or more parties without the need for a third-party intermediary. Funds transfers are used to transfer money between two individuals or entities using electronic funds transfers. Payment processors allow users to securely accept payments from customers in digital currency. Smart contracts are digital agreements that are programmed into the blockchain and automatically executed according to certain predetermined conditions.
Blockchain technology is revolutionizing the way we access financial services and is transforming the way businesses transact. By offering greater security and transparency, blockchain-based financial services have the potential to revolutionize the way people make payments and manage their finances.
Blockchain technology has become increasingly popular in recent years due to its ability to provide secure, immutable and transparent data management. It enables the secure transfer of ownership of digital assets, as well as a clearer view of supply chain operations and data sharing. This has made it a potentially powerful tool for supply chain management.
Supply chain management is a complex process that requires the coordination of multiple parties. Blockchain technology is well-suited to help streamline this process by providing a secure, tamper-proof ledger for the exchange of goods between buyers and sellers. This can help reduce costs and improve efficiency by eliminating redundant data entry and reducing the number of intermediaries involved.
Blockchain can also help improve visibility and traceability across the supply chain. Through blockchain-enabled IoT devices, stakeholders can track shipments in real time, allowing them to quickly identify where problems occur and make corrective actions as needed. This increased visibility can also be useful for compliance with regulatory requirements by providing an immutable record of each step in the supply chain process.
In addition, blockchain technology can provide a way to securely store and access product data, such as expiration dates and batch numbers. This makes it easier for companies to monitor product quality and ensure that their products meet safety standards. It can also be used to securely store contracts and agreements between different parties in the supply chain, making transactions more efficient and transparent.
The potential benefits of blockchain in supply chain management are clear. With its ability to provide secure, immutable data management and improved visibility, it has the potential to revolutionize how businesses coordinate shipments, manage contracts and track product quality. As more companies get on board with this emerging technology, the industry could see major gains from blockchain-enabled supply chain management in the future.

The healthcare industry is advancing rapidly and there are many new technologies coming out to improve the delivery of patient care. One such technology is blockchain, a system that provides secure storage and transfer of records. Blockchain is being increasingly used in the healthcare sector to store and manage patient records, track medical supplies, authenticate data, and increase the efficiency of clinical trials.
Blockchain technology offers a secure and decentralised structure to store healthcare records. It works on a distributed system where all participants have a copy of the data. This ensures that the data remains safe and secure, even if a malicious actor attempts to delete or alter it. Additionally, because blockchain stores immutable records, the risk of data manipulation is reduced significantly. This makes it a much better way to store sensitive healthcare information than traditional systems.
Blockchain can also help authenticate data in the healthcare sector. Patient records can be verified by other participants in the network, reducing the risk of forgery or falsification. Blockchain also reduces the chances of double-spending of medical supplies, as all transactions must be recorded and tracked on the distributed ledger. This helps ensure that medications are only purchased from approved sources.
Finally, blockchain technology can help speed up clinical trials by providing an efficient way to store and analyse patient data. Real-time analyses of large datasets can be conducted on blockchain, allowing researchers to quickly identify trends in treatments or medications without having to wait for lengthy paper-based paperwork processes. This increases the efficiency of clinical trials, allowing them to be completed much faster than before.
In conclusion, the healthcare industry is starting to embrace blockchain technology as a way to improve its operations. From secure storage of records to authentication of data and speeding up clinical trials, blockchain offers a number of advantages that make it an attractive solution for healthcare organisations. As more hospitals and clinics adopt this technology, we can expect to see even more efficiency and better patient outcomes as a result.
Blockchain technology has the potential to revolutionize the way we do business, but it also comes with a set of unique challenges. As businesses start to explore the opportunities of blockchain, they should also be aware of the challenges associated with its adoption. In this article, we’ll discuss some of the major challenges that businesses must address when implementing blockchain solutions.
1. Security Risks: Blockchain technology is decentralized, which means it operates on a distributed network instead of relying on individual central servers. Although this type of architecture offers high levels of security, it can also present certain risks such as potential malicious attacks on the network. Businesses must have robust security protocols in place to protect their data and ensure its integrity.
2. Cost and Complexity: As with any new technology, implementing a blockchain solution can be costly and complex. Companies need to weigh the benefits of using blockchain versus the cost of implementation to determine if it’s worth pursuing.
3. Scalability: Blockchain technology is not yet able to handle large amounts of data or high transaction volumes. As the technology evolves, businesses should be able to handle stronger workloads, but until then they must plan accordingly to ensure their system doesn’t become overloaded or experience delays.
4. Regulation: Governments around the world are still trying to figure out how to regulate blockchain-based systems. Businesses need to pay close attention to changes in regulations as they will have an impact on their operations.
5. Lack of Education: There is still a lack of education and understanding surrounding blockchain technology, which can make it difficult for businesses to find qualified individuals who are knowledgeable about this topic. Companies need to invest in training and development programs to ensure their employees are up to speed with the latest trends in blockchain technology.
Blockchain has the potential to transform industries, but businesses must prepare for the unique challenges associated with adoption. By understanding and addressing the issues discussed above, companies will be better positioned to capitalize on this new technology and drive innovation and growth within their organizations.

Blockchain technology is one of the most important and rapidly evolving technological advancements of our time. As the world continues to move forward with its digital transformation, blockchain has become an essential tool for secure and efficient data transfer. As a result, scalability has emerged as a major goal for developers and researchers. Scalability holds the potential to make blockchain more accessible to businesses and individuals who need it and can yield improved performance when compared to traditional databases.
Scalability in blockchain can be defined as the capability of a system to handle larger workloads than it currently does without compromising its performance or responsiveness. The rationale behind scalability is that it can help improve the user experience by allowing users to do more with their blockchain networks faster, cheaper, and more effectively. The scalability problem is one of the biggest challenges facing blockchain today, because the underlying protocol must be sufficiently robust to accommodate a high volume of transactions without any delays or errors.
When considering scalability, it’s important to focus on two primary aspects. First, scalability must be determined in terms of how many transactions can occur within a given timeframe. This means determining the maximum throughput of the system and ensuring that it’s able to process new transactions quickly enough for users to not experience any significant delays. Second, scalability must also consider the size of a blockchain network. If a network is too complex, it will become difficult to process transactions efficiently, leading to slower performance.
To improve scalability, developers have proposed multiple strategies. One approach is to increase the number of nodes in a blockchain network. This allows more machines to process transactions simultaneously and leads to increased throughput. Additionally, developers are exploring ways to improve network efficiency by using technologies such as sharding and state channels. Sharding divides large workloads into smaller pieces which can be processed more quickly and with less latency than if they were processed in their entirety. Similarly, state channels improve transaction speeds by allowing participants to bypass the blockchain ledger while still having all of the necessary data required to complete a transaction quickly and securely.
Another strategy is employing side-chains, which are alternative blockchains that are linked to the main blockchain in order to improve overall scalability. Side-chains can serve as a way for users and businesses to scale up their operations without overburdening the main chain’s capacity. For example, if a company needs to store large amounts of data, they can use a side-chain to store it and then send only relevant information back to the main chain when needed.
Ultimately, as blockchain technology continues to evolve, so too must its scalability capabilities. With the right strategies, developers have the potential to make blockchain truly accessible and beneficial for businesses and individuals alike. With further refinement, blockchain can become an even more powerful tool for secure and efficient data transfer in an increasingly digital world.
Blockchain technology is a revolutionary method of data storage and transfer that is fundamentally changing the way we conduct business. Blockchain is a distributed ledger technology that uses encryption to store, share and verify information.
At its core, blockchain technology is an immutable record-keeping system that operates in a decentralized manner. It serves as a repository for transaction records and other information related to digital assets. The data is stored across multiple computer nodes, making it extremely difficult to tamper with or change by any single party. Every transaction is cryptographically secured, which ensures the authenticity and reliability of records.
Blockchain technology has far-reaching implications for both businesses and individuals. For businesses, it presents opportunities to process transactions faster, streamline operations and strengthen security measures. For individuals, blockchain technology provides greater access to financial services, greater transparency into global markets, and enhanced trust in digital assets.
In addition to its use for financial services, blockchain technology can also be used in a variety of other contexts such as manufacturing, healthcare, supply chain management and more. Its potential is vast and can revolutionize many industries as we know them.
Though still in its infancy, blockchain technology already has the potential to bring about serious changes to the way we do business. Those who embrace the opportunities presented by this powerful technology will find themselves in a strong position to benefit from it.
Blockchain technology is a distributed database that allows for secure, transparent and tamper-proof transactions. It is the technology that underpins the cryptocurrency Bitcoin, but its potential uses go far beyond that.
2. How does Blockchain work?
A blockchain is a distributed database that allows for secure, transparent and tamper-proof transactions. Transactions are verified by a network of computers and recorded in a public ledger. This ledger is distributed across a network of computers, meaning that it is not controlled by any one party and is therefore secure from tampering.
3. What are the benefits of Blockchain technology?
The benefits of Blockchain technology include:
-Security: Blockchain is a tamper-proof database, meaning that transactions cannot be altered once they have been verified and recorded. This makes it a secure and reliable way to conduct transactions.
-Transparency: All transactions on a blockchain are public and can be viewed by anyone. This transparency ensures that transactions are fair and accurate.
-Efficiency: Blockchain technology can streamline transactions and reduce the need for third-party intermediaries. This can save time and money for businesses and consumers.
-Autonomy: Blockchain technology is decentralized, meaning that it does not rely on a third party to verify transactions. This gives businesses and consumers more autonomy and control over their transactions.
The world has changed in dramatic ways over the past decade with the introduction of blockchain technology. After all, blockchain is no longer just a buzzword or something limited to cryptocurrencies; it’s also become a legitimate technology that can be used to solve real-world problems. Businesses can now use blockchain technology to improve their operations, reduce costs, and increase security and trust. But what exactly are the benefits of blockchain technology for business?
1. Improved Security: One of the biggest advantages of blockchain technology is that it offers improved security compared to traditional systems. This is because blockchain networks use cryptography to provide strong security and protect data from unauthorized access. Additionally, transaction records are immutable and are stored in a decentralized ledger that is distributed across multiple computers. This helps to ensure that data is not vulnerable to manipulation or hacking as it is virtually impossible to alter or delete data once it is recorded on the ledger.
2. Increased Transparency: Another benefit of blockchain technology is increased transparency. As all transactions are recorded in an immutable ledger, the entire history of a transaction is visible to all users on the network. This helps to ensure that there is no fraud, double-spending, or other deceptive practices taking place within the network. Furthermore, as each transaction is visible to all users, businesses can easily track and trace each activity as it takes place.
3. Reduced Costs: Blockchain technology also helps businesses reduce costs as it eliminates the need for middlemen or third-party intermediaries who are traditionally responsible for verifying and settling transactions. This helps businesses save time and money by reducing administrative costs associated with manual processing and verifying of transactions. Furthermore, blockchain-based systems tend to be faster than traditional payment methods, which further reduces processing times and associated costs.
4. Improved Efficiency: Another major benefit of blockchain technology is improved efficiency as it enables faster, more secure transactions than traditional methods. Smart contracts, for example, allow businesses to automate business processes and reduce manual error. Additionally, blockchain’s distributed ledger system ensures that data remains consistent across all participants in the network, eliminating the need for manual reconciliation processes.
5. Increased Traceability: Finally, another key benefit of blockchain technology is its ability to provide increased traceability. As all transactions are securely stored on an immutable ledger, businesses can easily trace their transactions back to their source and verify their accuracy. This provides businesses with greater confidence in their transactions and helps them better manage their supply chains as they can easily identify any discrepancies or fraudulent activity along the way.
Overall, blockchain technology provides numerous benefits for businesses across various industries, from improved security and transparency to improved efficiency and traceability. As such, it’s no surprise that many businesses have already begun exploring how they can leverage this revolutionary technology to enhance their operations and stay ahead of their competition.

There are many benefits of blockchain technology. Some of these benefits include:
1. Increased security – One of the key benefits of blockchain technology is that it is inherently more secure than traditional databases. This is because blockchain technology uses a distributed ledger system, which means that data is stored across a network of computers rather than a single server. As a result, it is much more difficult for hackers to gain access to this data.
2. Increased efficiency – Blockchain technology can also help to increase efficiency and reduce costs. This is because it allows businesses to streamline their processes and reduce the need for intermediaries.
3. Increased transparency – Blockchain technology is also highly transparent, which means that businesses and individuals can track transactions and activity on the blockchain very easily. This can help to build trust and transparency between businesses and customers.
4. Increased speed – Blockchain technology is also very fast, which means that transactions can be completed quickly and easily. This can be particularly beneficial for businesses that operate in a fast-paced environment.
Blockchain technology has taken the world by storm over the past few years. It is a revolutionary way to store data and transfer information securely, providing a secure and efficient platform for conducting financial transactions, verifying identities, and ensuring transparent data management.
The application of blockchain technology is far-reaching, and its potential to revolutionize multiple industries is well recognized. Here are some of the most common applications of blockchain technology:
1. Financial services: Blockchain technology is primarily used to facilitate secure and fast financial transactions on a global scale. It has been adopted by many financial institutions for its ability to process large amounts of data quickly, securely, and without errors. This has enabled hassle-free transactions between parties, such as money transfers, asset exchanges, and more.
2. Smart contracts: Smart contracts are digitized contracts that are automated via blockchain technology. They are designed to ensure that agreements are executed precisely according to contract terms while also providing additional security and transparency.
3. Supply chain management: Blockchain technology can be used in supply chain management to create an immutable record of the transfer of goods between different parties or countries. This ensures that goods are not counterfeit, stolen, or damaged in transit.
4. Identity verification: Using blockchain technology, companies can verify the identities of customers without having to store personal information. This type of identity verification is becoming increasingly important as organizations try to protect their customers’ information from being compromised.
5. Voting: Blockchain technology can be used in voting systems to provide an immutable and secure voting mechanism that ensures that all votes are counted accurately and transparently.
6. Healthcare: Healthcare organizations are beginning to use blockchain technology to securely store health records and other sensitive patient information. Using blockchain technology in conjunction with AI technologies can provide more accurate diagnoses and treatment plans.
To summarize, blockchain technology is beginning to revolutionize how we conduct business and manage our data by providing secure, efficient, and transparent systems that allow us to securely transfer information and assets while also protecting our identities. Its potential applications are vast, and its ability to revolutionize multiple industries cannot be underestimated.
in Business
The blockchain is a distributed database that allows for secure, transparent and tamper-proof transactions. It is often described as a distributed ledger, meaning that data is stored and verified by a network of computers rather than a centralized authority. This makes the blockchain an ideal technology for businesses that need to share data securely and transparently.
The blockchain can be used to create a secure, transparent and tamper-proof ledger of transactions. This can be used to track the movement of goods, to verify the identity of customers or to record the steps in a business process. The blockchain can also be used to create digital contracts that are automatically enforced by the blockchain.
The blockchain can be used to create a secure, transparent and tamper-proof ledger of transactions.
The blockchain is also a distributed computing platform, which means that businesses can use it to create their own applications. These applications can be used to improve the efficiency of business processes or to create new business models.
The blockchain has the potential to revolutionize the way businesses operate. It can be used to create a secure, transparent and tamper-proof ledger of transactions, which can improve the efficiency of business processes. The blockchain can also be used to create applications that can be used to improve the efficiency of business processes or to create new business models.
Blockchain technology has revolutionized the world of technology and finance, offering a secure, transparent, and streamlined system for record keeping and asset exchange. However, the emergence of blockchain technology also introduces a wide range of challenges, from legal issues to security considerations.
Legal challenges of blockchain technology include jurisdictional issues with cross-border transactions, as well as challenges to existing regulatory structures. This is due to decentralized nature of blockchain transactions, which are often global in scope, leaving regulators grappling with how to regulate these new types of transactions. Additionally, the way in which blockchain technologies store data can make it difficult to adhere to laws regarding data privacy and protection. Clarity on these issues is needed in order for blockchain technology to be used effectively.
There are also technical challenges associated with blockchain technology. Many traditional networks rely on centralized databases, while blockchain technology is decentralized. This can lead to scalability issues as the network grows, as nodes must process a large amount of data in order to keep the chain up and running. Additionally, due to the distributed nature of blockchain technology, the trust between users may be lacking and consequently, less reliable than other networks.
Security is another major challenge for blockchain technology. The decentralized nature of the technology makes it vulnerable to attacks from hackers, who may be able to access vital information stored in the blockchain. Additionally, as the network grows, it may become more difficult to track changes in the data, making it easier for malicious actors to tamper with or manipulate stored information.
Finally, there is an element of cognitive overload associated with blockchain technology. New users can find it difficult to understand the technical aspects of the systems, leading to errors in implementation. This can be mitigated with education and training, but many users struggle with the basics of blockchain technology and consequently make costly mistakes.
In conclusion, while blockchain technology offers a whole range of benefits and advantages, its adoption is hampered by a number of unique challenges. From legal uncertainty to security risks and cognitive overload, developers must be careful when considering this new technology. While solutions exist for most of these problems, they require close attention in order to ensure that blockchain technology can reach its full potential.
The blockchain technology is still in its nascent stages and faces several challenges. One of the key challenges is scalability. The blockchain technology can only process a limited number of transactions per second. This is because of the way the blockchain technology works. The blockchain technology is a distributed database that is maintained by a network of computers. When a new transaction is added to the blockchain, all of the computers in the network must approve it. This approval process slows down the transaction process.
Another challenge facing the blockchain technology is security. The blockchain technology is still susceptible to hacking. In addition, the blockchain technology is not very user friendly. It is difficult for non-technical users to understand how to use the blockchain technology.
Blockchain technology is rapidly emerging as one of the most revolutionary developments of the 21st century, with powerful potential to revolutionize a myriad of industries and areas of life. It has been lauded as a revolutionary technology and is being explored by multiple industries as a means to streamline processes and securely store data. As such, numerous people are asking what the future of blockchain technology holds, and how it could shape our lives in the years to come.
First and foremost, blockchain technology is likely to become an integral part of the financial system. This is because the distributed ledger technology, which blockchain employs, eliminates the need for third party verification and trust in transactions. This reduces the opportunity for fraud and simplifies the process of completing transactions. Furthermore, the use of smart contracts ensures that payments are made in real time, further streamlining the process. This will be beneficial to individuals, businesses, and financial institutions alike.
Second, blockchain technology could be used to increase security across a variety of sectors. For example, it could be employed to ensure that citizens’ personal information remains secure in government databases as well as health care. Additionally, blockchain technology could also be used in energy grids to ensure that data remains secure and accurate and to ensure that participants are appropriately incentivized for their contribution to energy production.
Third, blockchain technology could revolutionize supply chain management. Currently, supply chains often rely on manual processes and have no central system of record keeping. This makes it difficult to track information about the source and movement of goods across the supply chain. Blockchain technology could provide a reliable method of recording data, allowing businesses to track everything from where the product was sourced to who is handling it at what stage. This would also make it easier for businesses to identify bottlenecks as well as fraud or mistakes within the system.
Finally, companies are beginning to explore how blockchain technology can be used to protect intellectual property. Companies can create digital certificates that represent ownership of physical assets such as real estate, artworks, or even music compositions. As such, users can prove ownership without having to physically transfer documents or materials. This could reduce disputes and make it easier for users to transfer assets in a secure way.
Ultimately, blockchain technology has powerful potential to shape our lives in the years to come. It could revolutionize a number of sectors from finance to energy grids and from supply chain management to intellectual property protection. The possibilities are endless and it is clear that we are just beginning to scratch the surface of its potential power.

The blockchain is a distributed database that allows for secure, transparent and tamper-proof transactions. The technology is still in its early stages, but it has already garnered a lot of attention from businesses and investors. Here are some of the ways that blockchain technology is expected to grow in the future:
1. Increased Use in Commercial Transactions:
The blockchain is well-suited for commercial transactions because it allows for secure and transparent transactions. The technology can be used to create a permanent, tamper-proof record of transactions. This can be helpful for businesses that want to track the flow of money and goods.
2. Increased Use in the Public Sector:
The blockchain can be used to improve transparency and accountability in the public sector. The technology can be used to create a permanent record of government transactions and to track the distribution of government benefits.
3. Increased Use in the Financial Sector:
The blockchain is already being used in the financial sector to create secure and transparent transactions. The technology can be used to streamline the process of issuing and tracking financial transactions.
4. Increased Use in the Healthcare Sector:
The blockchain can be used to securely store and share healthcare data. The technology can be used to create a permanent, tamper-proof record of patient data. This can help to improve the security and efficiency of the healthcare system.
5. Increased Use in the Retail Sector:
The blockchain can be used to improve the security of the retail sector. The technology can be used to create a permanent record of transactions and to prevent fraudulent transactions.
The blockchain is a promising technology that is expected to grow in popularity in the future. The technology has already garnered a lot of attention from businesses and investors, and it is likely to continue to grow in popularity in the years to come.
You cannot copy content of this page