NEOM: Unlocking the Future of Sustainable Liv
I. Introduction NEOM is a $500 billion, 26,500 square ...
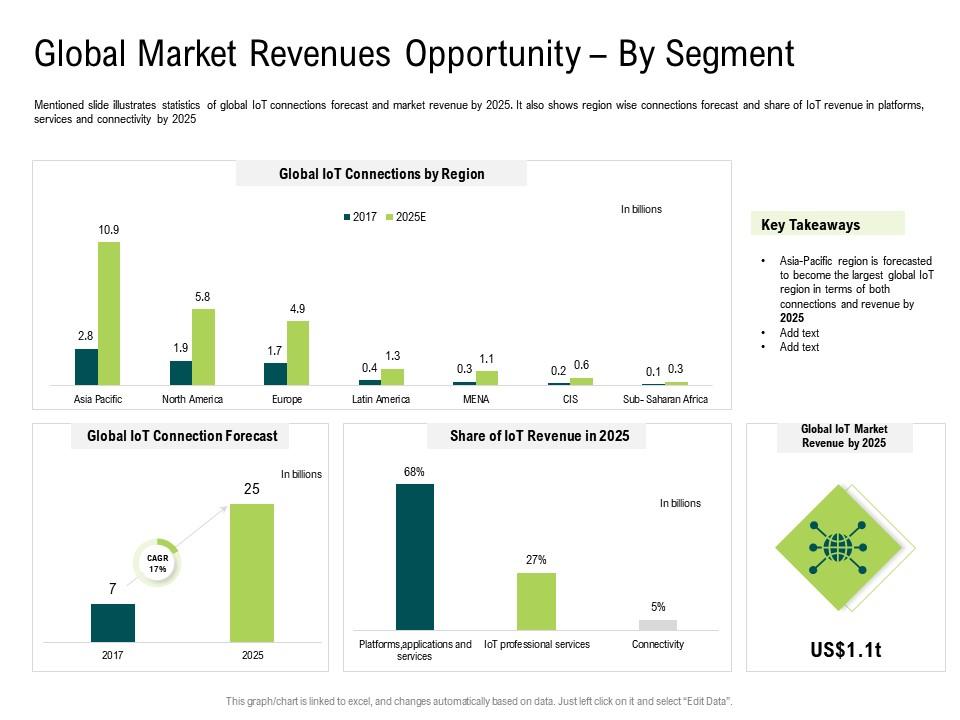
The Internet of Things (IoT) is a network of physical devices, vehicles, home appliances, and other items that are embedded with electronics, software, sensors, and connectivity that enable these objects to connect and exchange data. By 2020, it is estimated that there will be more than 26 billion connected devices,1 all of which will be collecting and sharing data about everything from our daily routines to the inner workings of our homes and cities. This data can be used to improve our lives in a variety of ways, from making our daily commute more efficient to reducing energy consumption.
In many ways, the IoT is already making our lives more connected. For example, many of us now use fitness trackers that collect data about our daily activity levels and sleep habits. This data can be used to improve our health by helping us to better understand our sleep patterns and activity levels. The IoT can also help us to be more efficient in our daily lives. For instance, imagine you are running late for a meeting and forgot to turn off the lights in your office. With the IoT, you could use your smartphone to remotely turn off the lights, saving you time and energy.
The IoT also has the potential to make our cities more efficient. For example, sensors embedded in trash cans could let city workers know when they need to be emptied, saving time and labor. Similarly, sensors could be used to monitor traffic patterns and adjust traffic signals accordingly, reducing congestion and improving travel times.
Of course, the IoT is not without its challenges. One of the biggest challenges is security. As more and more devices are connected to the internet, there is an increased risk of hacking and data breaches. Additionally, the vast amount of data being collected by IoT devices could potentially be used to invade our privacy. For example, our smart TVs could be tracking our viewing habits and selling that data to advertisers.
Another challenge facing the IoT is interoperability. In order for the IoT to reach its full potential, devices from different manufacturers need to be able to communicate with each other. Unfortunately, this is often not the case. As a result, many devices are siloed and unable to work together, limiting the potential of the IoT.
Despite these challenges, the IoT is poised to have a major impact on our lives in the years to come. As more and more devices are connected to the internet, we will increasingly reap the benefits of a more connected world.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/FinancialTechnology_Final_4196400-e038b8e499c94ae3ac2ba5e843f86546.png)
The Internet of Things, often shortened to IoT, is a network of physical devices, vehicles, home appliances and other items that are embedded with electronics, software, sensors and connectivity enabling them to connect, collect and exchange data.
IoT describes a future where everyday physical objects will be connected to the Internet and be able to identify themselves to other devices. The IoT is a giant network of connected “things” and people. Each thing has a unique identifier and is able to transfer data over a network without requiring human-to-human or human-to-computer interaction.
IoT devices can range from something as small as a sensor embedded in a shoe, to a car with dozens of sensors collecting data about the environment and the driver’s behavior. Other examples of IoT devices include:
Smart home devices like thermostats, security systems and lighting
Wearable devices like fitness trackers and smartwatches
Medical devices like pacemakers and glucose monitors
Industrial equipment like sensors on assembly lines and machines in factories
Commercial applications like retail sensors that track customer behavior
The possibilities for the IoT are nearly limitless. By 2020, it is estimated that there will be over 50 billion connected devices worldwide.
The Benefits of the IoT
The IoT has the potential to transform the way we live, work and play. Here are just a few of the ways the IoT can make our lives better:
Increased efficiency and productivity: The IoT can help businesses become more efficient and productive by automating tasks and collecting data that can be used to make better decisions.
The IoT can help businesses become more efficient and productive by automating tasks and collecting data that can be used to make better decisions. Improved safety and security: The IoT can help keep people safe by providing real-time information about potentially dangerous situations. For example, connected cars can warn drivers about accidents ahead, and smart home security systems can alert homeowners about intruders.
The IoT can help keep people safe by providing real-time information about potentially dangerous situations. For example, connected cars can warn drivers about accidents ahead, and smart home security systems can alert homeowners about intruders. Greater convenience: The IoT can make our lives more convenient by giving us access to information and controls when we need them. For example, we can use our smartphones to unlock our doors, turn off the lights or start the coffee pot before we even get out of bed.
The IoT can make our lives more convenient by giving us access to information and controls when we need them. For example, we can use our smartphones to unlock our doors, turn off the lights or start the coffee pot before we even get out of bed. More personalized experiences: The IoT can provide more personalized experiences by collecting data about our preferences and tailor content and services accordingly. For example, your music streaming service could suggest new songs based on the music you’ve listened to in the past, or your hotel could adjust the temperature in your room to your preferred settings as soon as you check in.
The Challenges of the IoT
Despite its many benefits, the IoT also poses some challenges that need to be addressed:
Security and privacy: The IoT collects large amounts of data about our activities and location. This raises concerns about how this data will be used and who will have access to it. Without proper security measures in place, the IoT could be used to enable cyber attacks or invade our privacy.
The IoT collects large amounts of data about our activities and location. This raises concerns about how this data will be used and who will have access to it. Without proper security measures in place, the IoT could be used to enable cyber attacks or invade our privacy. Interoperability: The IoT is composed of a large number of devices from different manufacturers. These devices need to be able to work together seamlessly in order to realize the full potential of the IoT. However, this is often not the case due to incompatibilities between devices.
The IoT is composed of a large number of devices from different manufacturers. These devices need to be able to work together seamlessly in order to realize the full potential of the IoT. However, this is often not the case due to incompatibilities between devices. Standardization: In order for the IoT to reach its full potential, there needs to be a standardization of technologies, protocols and interfaces. Without standardization, the number of devices that can connect to the IoT will be limited, and the IoT will remain fragmented.
In order for the IoT to reach its full potential, there needs to be a standardization of technologies, protocols and interfaces. Without standardization, the number of devices that can connect to the IoT will be limited, and the IoT will remain fragmented. Scalability: The IoT is growing at an exponential rate. This presents a challenge for developers who need to create applications that can scale to meet the demands of a large number of devices.
The Future of the IoT
The IoT is still in its early stages, but it is already having a profound impact on our lives. In the future, the IoT will become even more ubiquitous and integrated into every aspect of our lives. We will see more connected devices, smarter applications and new business models that take advantage of the vast amounts of data generated by the IoT.
The phrase “Internet of Things” (IoT) has been around since the early 1990s, but it has only recently begun to enter the mainstream vernacular. The rapid expansion of the Internet and the proliferation of wireless devices has driven the development of the IoT and its growing impact on our lives.
At its most basic level, the IoT refers to the network of physical objects that are connected to the internet. These objects can include anything from wearable devices and home appliances to industrial equipment and vehicles. The IoT allows these objects to collect and exchange data with one another and with the outside world.
The potential applications of the IoT are endless. Some of the most common applications include:
• Remote monitoring and tracking of objects and assets
• Remote diagnostics and fault detection
• Smart homes and cities
• Intelligent transportation and logistics
• Predictive maintenance
1.2 How does the IoT work?
The IoT is made up of three core components: devices, connectivity, and applications.
Devices are the physical objects that are connected to the internet. These objects can include anything from wearable devices and home appliances to industrial equipment and vehicles.
Connectivity is the technology that allows devices to connect to the internet. This can include wired or wireless connections, and can be local or global.
Applications are the software that enables devices to communicate and interact with one another. Applications can be used to collect and analyze data, or to control and monitor devices.
1.3 Why is the IoT important?
The IoT is important because it enables devices to connect and interact with one another. This allows objects to collect and exchange data, which can be used to improve our lives and our businesses.
The IoT has the potential to revolutionize the way we live and work. It can help us to:
• Reduce energy consumption
• Improve traffic flow and reduce congestion
• Enhance safety and security
• Improve productivity and efficiency
• Reduce costs
The IoT is also important because it is creating a new economy known as the “Industry 4.0”. This is an economy that is based on the interconnectedness of devices, data, and people. It is an economy that is driven by the rapid expansion of the IoT and the growth of digital technologies.
The Internet of Things (IoT) is a system of physical devices, vehicles, home appliances and other items that are embedded with electronics, software, sensors, and connectivity enabling them to collect and exchange data. The IoT allows these objects to connect and interact with each other and with the external environment using the internet.
The term “Internet of Things” was first coined by Kevin Ashton in 1999 while working on RFID technology. Since then, the IoT has evolved into a network of billions of devices that are connected to the internet. These devices can include anything from everyday objects like fridges and light bulbs, to more complex systems like industrial machines and vehicles.
IoT devices are able to collect and exchange data using a variety of means including Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, NFC, cellular networks and more. The data collected by IoT devices can be used to monitor and manage various systems and processes. For example, data from an IoT sensor attached to a machine could be used to track the machine’s performance or detect potential problems.
The IoT has the potential to revolutionise many industries and aspects of our lives. For example, the healthcare sector could use IoT devices to monitor patients’ vital signs and provide early warning of any potential health issues. In the transportation sector, the IoT could be used to manage traffic flows and reduce congestion. And in the home, the IoT could be used to automate tasks like turning off the lights when no one is in the room.
The potential applications of the IoT are virtually limitless. The key challenge now is to ensure that the devices are securely connected and that the data they exchange is properly protected.
The internet of things (IoT) is a term for the ever-growing network of devices that are connected to the internet. These devices can include anything from household appliances to industrial machinery.
The IoT is made possible by a technology called the “internet of things protocol”, which allows devices to communicate with each other and with computers. This protocol is based on a technology called “machine-to-machine communication”, which allows devices to send and receive data without the need for human interaction.
The IoT has many applications, including:
1. Home automation – the control of household appliances, such as lights, heating, and security systems, through a computer or mobile device.
2. Factory automation – the control of industrial machinery, such as robots, through a computer or mobile device.
3. Smart cities – the use of sensors and cameras to collect data on traffic, energy usage, and public safety, which can then be used to improve the efficiency of cities.
4. Health care – the use of sensors and monitors to track the health of patients, which can then be used to improve the quality of care.
5. Retail – the use of sensors and RFID tags to track the movement of goods, which can then be used to improve inventory management and customer service.
The IoT is still in its early stages, and the full potential of this technology has yet to be realized. However, it is clear that the IoT has the potential to change the way we live and work.
The Internet of Things, often abbreviated as IoT, refers to the growing trend of connecting physical objects to the internet. This includes everything from everyday household items like appliances and thermostats, to more complex systems like cars and industrial machinery. The IoT has the potential to transform the way we live, work, and play by making our lives more convenient, efficient, and safe. However, there are also some potential drawbacks to consider.
One of the main benefits of the IoT is that it can make our lives more convenient. For example, imagine you’re running late for an appointment and realize you left the oven on. With a smart oven connected to the internet, you could simply log in and turn it off from your phone. No need to worry about rushing home or asking a neighbor to check on things for you. Similarly, you could program your lights to turn on and off automatically based on your schedule, or receive an alert on your phone if someone enters your home while you’re away.
In addition to making our lives more convenient, the IoT can also help us be more efficient. For example, you could install sensors in your office to track how many people are using each room throughout the day. This information could then be used to optimize the heating and cooling of the space, or to re-arrange the furniture to create a more efficient layout. The IoT can also be used to help manage inventory levels, so that you only order as much as you need, when you need it. This can save both time and money.
Finally, the IoT has the potential to make our lives safer. For example, cars could be equipped with sensors that detect when a tire is low on air or when there’s an obstacle in the road. This information could then be used to automatically alert the driver or even take corrective action such as slowing down or changing lanes. In the home, smoke detectors and security cameras could be connected to the internet, so that you can monitor them from anywhere in the world and receive an alert if there’s a problem.
Despite all of these potential benefits, there are also some drawbacks to consider with the IoT. One of the biggest concerns is security. When physical objects are connected to the internet, they become potential targets for hackers. This could allow criminals to gain access to our personal information, or even take control of devices like cars and security cameras. There have already been a number of high-profile hacks of IoT devices, and this is likely to continue as the technology becomes more widespread.
Another potential issue is privacy. The more data that’s collected about our daily activities, the more potential there is for that information to be used without our knowledge or consent. For example, companies could use data collected by sensors in our homes to target us with ads, or insurance companies could raise rates based on information about our health or lifestyle. While some of this data may be anonymous, it’s becoming increasingly easy to link data back to individual people.
Finally, the IoT has the potential to create a lot of unnecessary clutter and complexity in our lives. As more and more devices are connected to the internet, it can be difficult to keep track of them all. We may also start to rely too much on technology, and lose the ability to do things for ourselves. For example, if our ovens are connected to the internet, we may not know how to cook without them.
The IoT has the potential to transform the way we live, work, and play. However, there are also some potential drawbacks that should be considered before embrace this technology fully.

The internet of things (IoT) is a term for the network of physical objects that are connected to the internet. These objects can include anything from appliances and vehicles to wearable devices and sensors.
The benefits of the IoT include increased efficiency, improved safety, and enhanced communication. For example, a factory can use IoT devices to track the production process and identify areas for improvement. A city can use IoT devices to improve traffic flow and reduce congestion. And a hospital can use IoT devices to improve patient care.
The drawbacks of the IoT include privacy concerns and security risks. For example, a hacker could gain access to sensitive information by hacking into an IoT device. Or a company could use IoT data to track people’s movements and activities.
Despite the benefits and drawbacks of the IoT, the trend is clearly moving in the direction of increased connectivity and interconnectivity. As more and more devices are connected to the internet, the potential for increased efficiency and innovation is limitless.
You cannot copy content of this page